2019-07-05T16:03:48
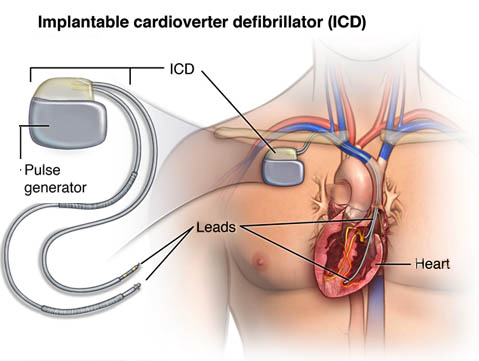
:Indian Heart Association Guidelines to primary prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death :- Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD) accounts for over half of cardiovascular mortality and is a major public health issue. The Indian Heart Association have released a guideline on primary prevention and control of SCDs in early and post Myocardial Infarction (MI). This guidelines aims at providing a contemporary guideline for the management of adults who have Ventricular Arrhythmia (VA) or who are at risk for SCD, including diseases and syndromes associated with a risk of SCD from VA. Sudden cardiac death (SCD)is generally understood by the lay and medical communities as sudden unexpected collapse, without warning. Ventricular Arrhythmia (VA) includes a spectrum of disease that ranges from the premature ventricular complex (PVC) to ventricular fibrillation (VF), with a clinical presentation that ranges from a total lack of symptoms to cardiac arrest. Most life threatening Ventricular Arrhythmia are associated with ischemic heart disease which is particularly seen in older patients. The risks of VA and SCD vary in specific populations with different underlying cardiac conditions, and with specific family history and generic variants, and this variation has important implications for studying and applying therapies. Following are the key recommendations of the guideline provided for primary prevention and control of SCD in patients with ventricular arrhythmia. With reduced EF (< 40%), follow guideline directed medical therapy (GDMT) to include : • Beta blockers; • Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; & • Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, or angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitors. • With life expectancy > 1 year, where GDMT fails to prevent the following, implanted cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) is recommended: 1. Left ventricular EF (LVEF) <= 35% and ischemic heart disease at 40+ days after myocardial infarction, 90+ days post – revascularization, class II – III heart failure. 2. LVEF <= 30% with ischemic heart disease at 40+ days after myocardial infarction, 90+ days post revascularization, class I heart failure; or 3. Nonischemic cardiomyopathy, class II – III symptoms, LVEF <= 35%. 4. Biggest guidelines change from earlier versions is the addition of angiotensin receptor- neprilysin inhibitors, which the synopsis authors say remains controversial. 5. Benefits for patients include the focus on GDMT before moving to ICD, with the parameter of expected survival > 1 year. We are known as “Centre for Excellence in Cardiology”. We have expert team of Cardiologist, Cardiac Surgeons, and Cardiac Anaesthetist who perform various cardiac procedures, available 24 X 7. We also provide Intensivists who handles critical cases with excessive care. For economically backward patients we are authorised with “Chief Minister Relief Fund” to benefit Angiography at Rs. 9999/- and Angioplasty at Rs. 99999/- . For further enquires please feel free to call us at 7350055754 – 7 Orange Hospital. Pawana nagar, Chapekar chowk, Chinchwad, Pune – 411033.